ISO 9001 requirements and structure: The essentials explained simply
If you are looking for a brief but powerful explanation of the requirements and structure of the ISO 9001 standard, you are in the right place.
In this blog, we explain how this standard is structured and what is required to implement it in your quality management system. In a few minutes, your basic knowledge as far as ISO 9001 is concerned will be fully up to date!
How is the ISO 9001 structured?
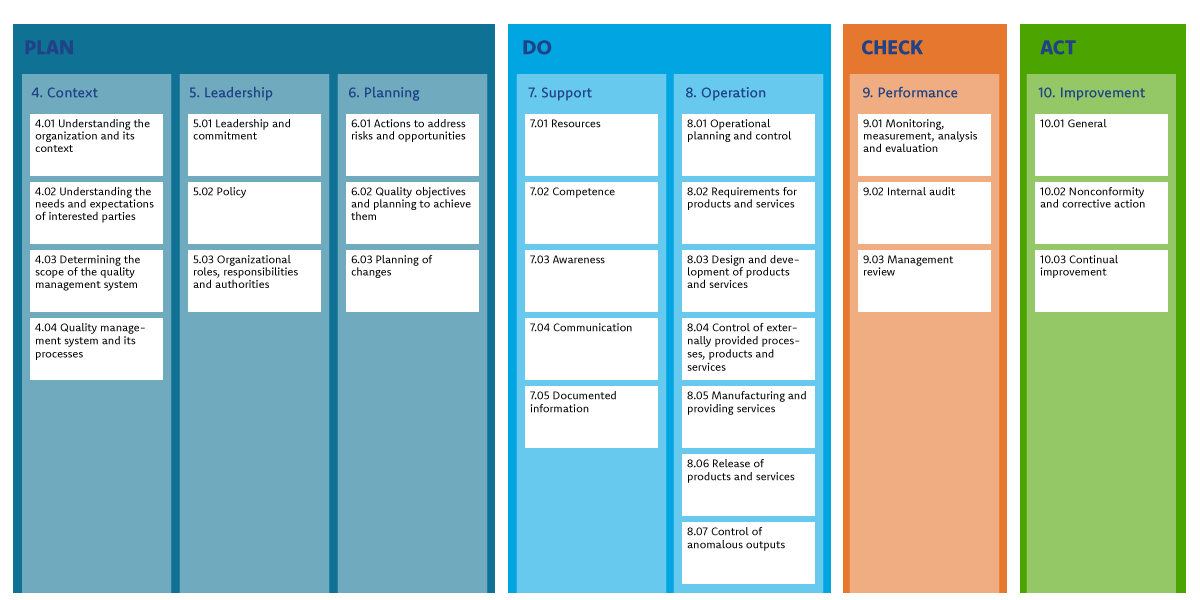
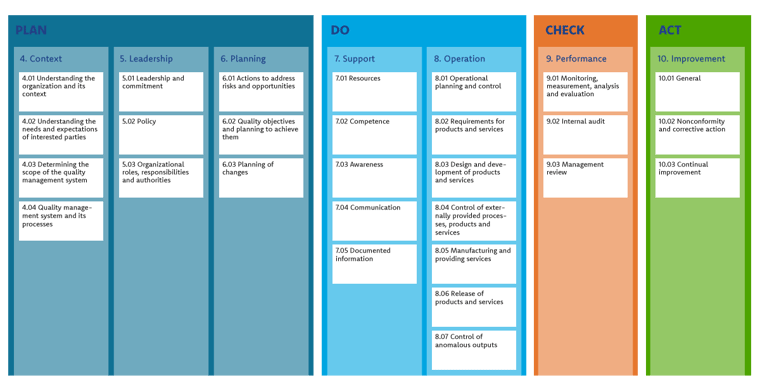
The chapters of the standard have a logical structure: they are based on the Deming Circle.
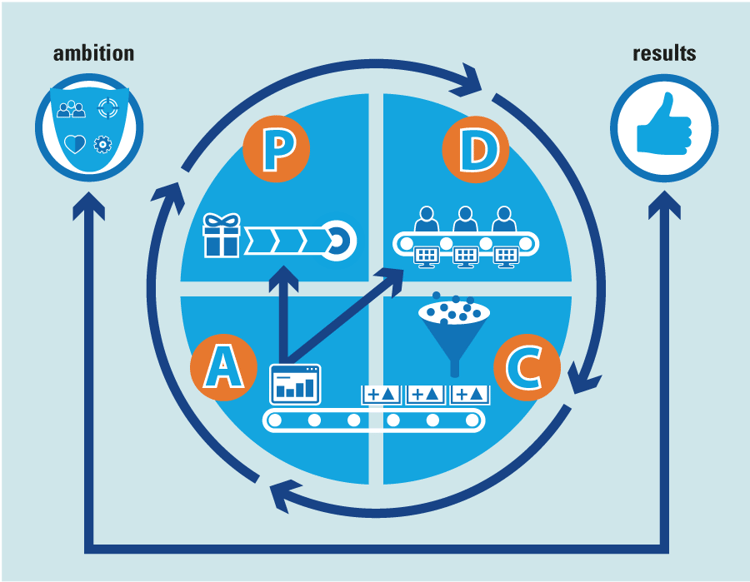
The Deming Circle is also known as Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA). Applied when setting up a quality management system that must comply with the ISO 9001 standard, the four phases look as follows:
- Plan (chapters 4 through 6): In this first phase, you consider what needs to be done to implement your quality management system. You determine where you want to grow as an organization, and determine the conditions for the organizational structure accordingly.
- Do (chapters 7 and 8): This is the phase where you actually start implementing your quality management system. This includes, for example, drafting work instructions or writing procedures.
- Check (chapter 9): Measure and evaluate whether the actions taken actually lead to the desired results. Here you pick up the objectives and conditions you drew up in the plan phase and use key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess where there is room or need for improvement.
- Act (chapter 10): Based on the outcomes in the check phase, respond appropriately to any undesirable outputs.
One of the most important aspects of a quality management system is that it is never "finished." The system must be continuously improved. Therefore, with the outcomes of the Act phase, the PDCA cycle starts all over again: where necessary, you will have to adjust your plan and adapt the corresponding processes, and then monitor whether the results are satisfactory.
Chapter 0: Introduction
This chapter introduces several key principles of the ISO 9001 standard, such as:
- The benefits of implementing a quality management system
- The process approach (which includes: SIPOC model (a schematic representation of a process and the interaction of the elements within it), the PDCA cycle and risk-based thinking)
- The 7 quality principles on which the standard is based
Chapters 1 to 3: Subject and scope, normative references, terms and definitions
The first three chapters of the standard are informative and do not contain specific requirements. ISO 9001 contains not only requirements that address quality assurance of products and services, but also requirements that help increase customer satisfaction.
Chapter 4: Context of the organization
Chapter 4 is the first chapter that contains specific requirements. An organization is not a closed system; it is constantly influenced by its environment.
Therefore, when implementing a quality management system, it is important to be aware of the context in which your organization finds itself.
The purpose of chapter 4 is to identify the context of the organization and set out a strategic direction in terms of quality.
Key requirements from Chapter 4:
- Stakeholder management: a requirement of ISO 9001 is that you identify who your stakeholders are and what their expectations are regarding the organization's performance.
- Risk management: an organization must identify risks and opportunities that may affect the quality of the product or services.
- In addition, you must determine to which portions of the organization the quality management system applies. Does the certification apply company-wide or is it only for sales and management and not for manufacturing, for example. The scope is stated on your ISO certificate.
Chapter 5: Leadership
This chapter concerns the responsibility of an organization's management. ISO 9001, through Chapter 5, requires the involvement of management in the implementation and improvement of the quality system.
Key requirements from Chapter 5:
- Management should be directly involved in the quality policy, not delegate it.
- Management is responsible for establishing a quality policy.
- Management is responsible for clear communication of the quality policy to the entire organization.
- Management ensures that everyone in the organization knows that he or she will be supported from top management to meet the requirements of the ISO 9001 standard.
- Management should define roles and responsibilities within the organization to ensure that the quality management system is managed effectively.
Chapter 6: Planning
Chapter 6 translates the risks and opportunities identified in Chapter 4 into concrete actions. Goals are set and plans are devised to actually achieve these goals.
Key requirements from Chapter 6:
- Actions should be scheduled to address relevant risks and opportunities.
- Measurable quality objectives should be established, communicated and measured periodically.
- If the quality management system is to be improved, consideration must be given to the changes required to do so (Management of Change). What are possible risks of the change, what resources are needed, who will implement the changes?
Chapter 7: Support
Chapter 7 deals with everything needed to deliver quality. The chapter is quite diverse and covers a variety of resources: from proper transportation to attention to employee knowledge levels.
Key requirements from Chapter 7:
- Provide the right resources to carry out the plans. Think employees, buildings, the right work environment, transportation, etc.
- Ensuring that attention is paid to knowledge and competence management. Employees may start requiring additional training and education for this purpose.
- Clearly communicating the quality policy and relevant objectives with each employee who contributes to the quality management system. For example, by providing company regulations, and through training and performance reviews.
- Documenting the information needed to carry out the quality processes, for example using quality management software such as Comm'ant.
Chapter 8: Operation
Time for action! Chapter 8 is about actually implementing the quality management system.
Key requirements from Chapter 8:
- Provide the operational planning necessary for execution.
- Ensure that the quality requirements your product or service must meet are defined.
- Design and describe processes needed to achieve the (new) quality goals. For example, using the Process Model Canvas. In doing so, also map out the control aspects.
- Make sure that the design and development process of the product is solid.
- Make sure that processes, products and services provided externally also meet your quality standard. Check all suppliers.
- Only transfer something to a customer if you are sure that it meets the quality standard.
If an output does turn out to be non-conforming, make sure you fix it.
Chapter 9: Performance evaluation
Let's verify that the quality management system is actually working as it should. This is done in Chapter 9.
Key requirements from Chapter 9:
- Determine what, how, when and by whom should be measured, analyzed and evaluated.
- Determine the methods for collecting, monitoring and assessing customer satisfaction.
- Conduct regular internal audits (internal audits) to determine continued compliance not only with its own established requirements, but also with the requirements from the ISO 9001 standard.
- Periodically review all measured performance and information provided by the ISO 9001 system and assess whether improvements should be made.
Chapter 10: Improvement
The last chapter of ISO 9001 is about continuous improvement. The goal is to never stop improving the quality management system.
Key requirements from Chapter 10:
- Identify and select opportunities for improvement
- Respond to deviations and take action to eliminate the cause
- Implement corrective actions where necessary and evaluate their effectiveness
- Keep track of these nonconformities and corrective actions
- Continuously improve your quality management system
Getting started with ISO 9001
Want to get started with a professional quality management system? Contact one of our ISO experts for an online demo. We will be happy to show you how to use Comm'ant - equipped with a complete library of standards - to quickly and effectively prepare your organization for certification.